Let’s talk about light bulbs.
Light bulbs can be used to key, fill, or backlight a subject. They can also be used as practicals to light a set. Inside every light is a burning element called the filament. Therefore, it is essential as a cinematographer to understand the different types of light bulbs and there characteristics.
The Quartz-Halogen bulb

The majority of interior location lighting fixtures use quartz halogen bulbs. These bulbs have a tungsten filament in it and are encased in a tiny glass made of quartz, which is filled with halogen gas. These bulbs can get really hot and be used in very small light fixtures. This particular bulb maintains a stable color output throughout its life. Long quartz halogen bulbs are made for fixtures that spread out light and diffuse it.
The HMI Light (Halogen Metal Iodide)
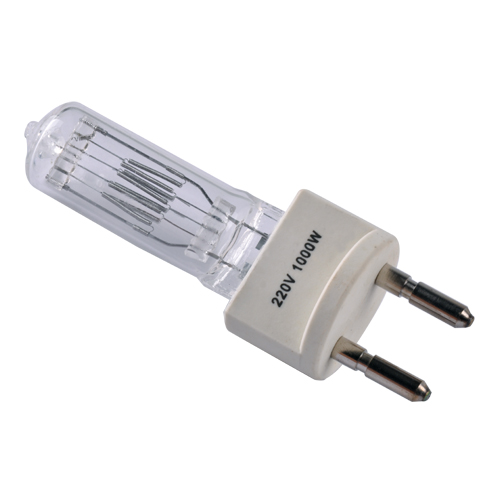

HMI lights produce a daylight color balanced temperature and are extremely efficient. It puts out three times more illumination in wattage then a tungsten bulb does with half the heat. These lights can be ran off of standard household current but need a ballast the keep the light running at a steady voltage. HMI lights also require time to warm up to temperature. Over time the color can shift with use.
The Tungsten-filament bulb

Standard household bulbs are tungsten lights and may not give you the punch that you need to key your subject. There are two types of tungsten-filament bulbs for film: photo bulbs and photofloods can give you the higher wattage you may need. They have the same screw-in base as Edison based bulbs. These lights are color balanced for indoors. Photofloods have built in reflectors so their illumination is much more directional.
Sodium Vapor bulb
A sodium-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses sodium. Street lamps are the most recognizable lighting fixtures that use sodium vapor lights. Sodium vapor lamps are highly efficient but they are also extremely yellow.
Metal Halide bulb
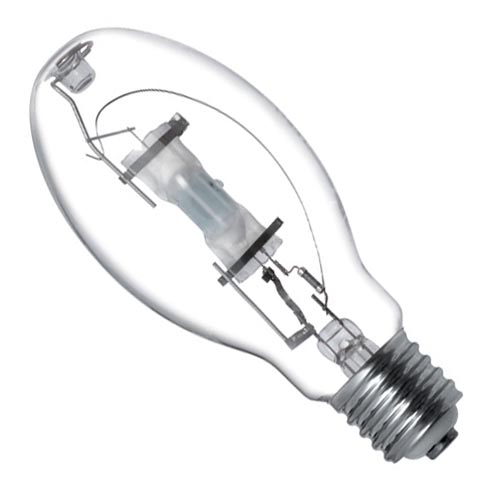

A metal-halide lamp is an electric lamp that produces light by an electric arc through a gaseous mixture of vaporized mercury and metal halides. Metal-halide lamps are 3-5 times more visible to the human eye and are commonly used for overhead lighting in commercial spaces, industrial, and public spaces, such as parking lots, sports arenas, factories, and retail stores, as well as residential security lighting and automotive headlamps.
It’s important to note that even though we are talking about bulbs, reflectors in lighting fixtures have a huge part in the quality of light. Reflectors that are textured can disperse the light in a greater area but smoother reflectors can give your lights more “punch.”
SAFETY TIP – It is very important to note that when you are changing light bulbs, you should wear gloves or use clothe. Light bulbs can reach extremely hot temperatures and the oil and residue left on fingers can cause light bulbs to explode.
If you enjoyed this article, let me know. Let me know with the community? Let me know. Join the Capturing Light Facebook community: https://www.facebook.com/groups/capturinglightcommunity/.