What is a sensor?
A sensor is a solid-state device which captures the light required to form a digital image. What essentially happens is that wafers of silicon are used as the base for the integrated circuit, which are built up via a process known as photolithography. This is where patterns of the circuitry are repeatedly projected onto the (sensitized) wafer, before being treated so that only the pattern remains. This is similar to traditional photographic processes, such as those used in a darkroom when developing film and printing.
It’s pretty scientific and there is a little math involved but sensors and crop factors are concepts you should know. If you are so inclined to do so, read more about sensors on wikipedia here.
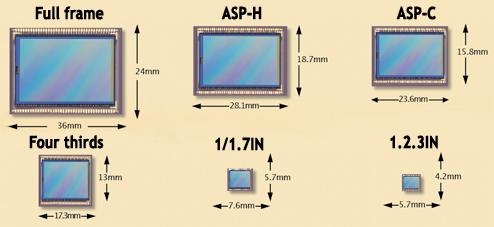
Full Frame – 36 x 24mm
Full Frame sensors are the largest sensor size found in 35mm DSLRs. It’s the equivalent of shooting a frame of 35mm negative film. Full frame sensors have no crop factor to lenses.
Camera example: Sony A7s
APS-H – 28.1 x 18.7mm
As featured in Canon’s 1D series of cameras. These typically combine the slightly larger sensor with a modest pixel count for speed and high ISO performance, and apply a 1.3x crop factor to mounted lenses.
Camera example: Canon 1D Mark IV
Super 35 – 24.89 x 18.66mm
A wide variety of motion picture cameras have a Super 35 sensor in them. Cameras such as: Arri Alexa, Sony F35, & Blackmagic Mini Ursa
APS-C – 23.6 x 15.8mm (varies)
The most common sensor size in consumer and semi-professional DSLRs, the APS-C sensor applies a crop factor between 1.5x to 1.7x to mounted lenses.
Camera example: Canon 7D Mark II
Four Thirds – 17.3 x 13mm
As used in both Four Thirds DSLRs and Micro Four Thirds models, these are roughly a quarter of the size of a full-frame sensor. Their size results in a 2x crop factor, doubling the effective focal length of a mounted lens.
Camera example: Panasonic GH4
Check out this video from FilmmakerIQ:
There are other sensor sizes out there, but these are the most popular in digital cameras being used today.